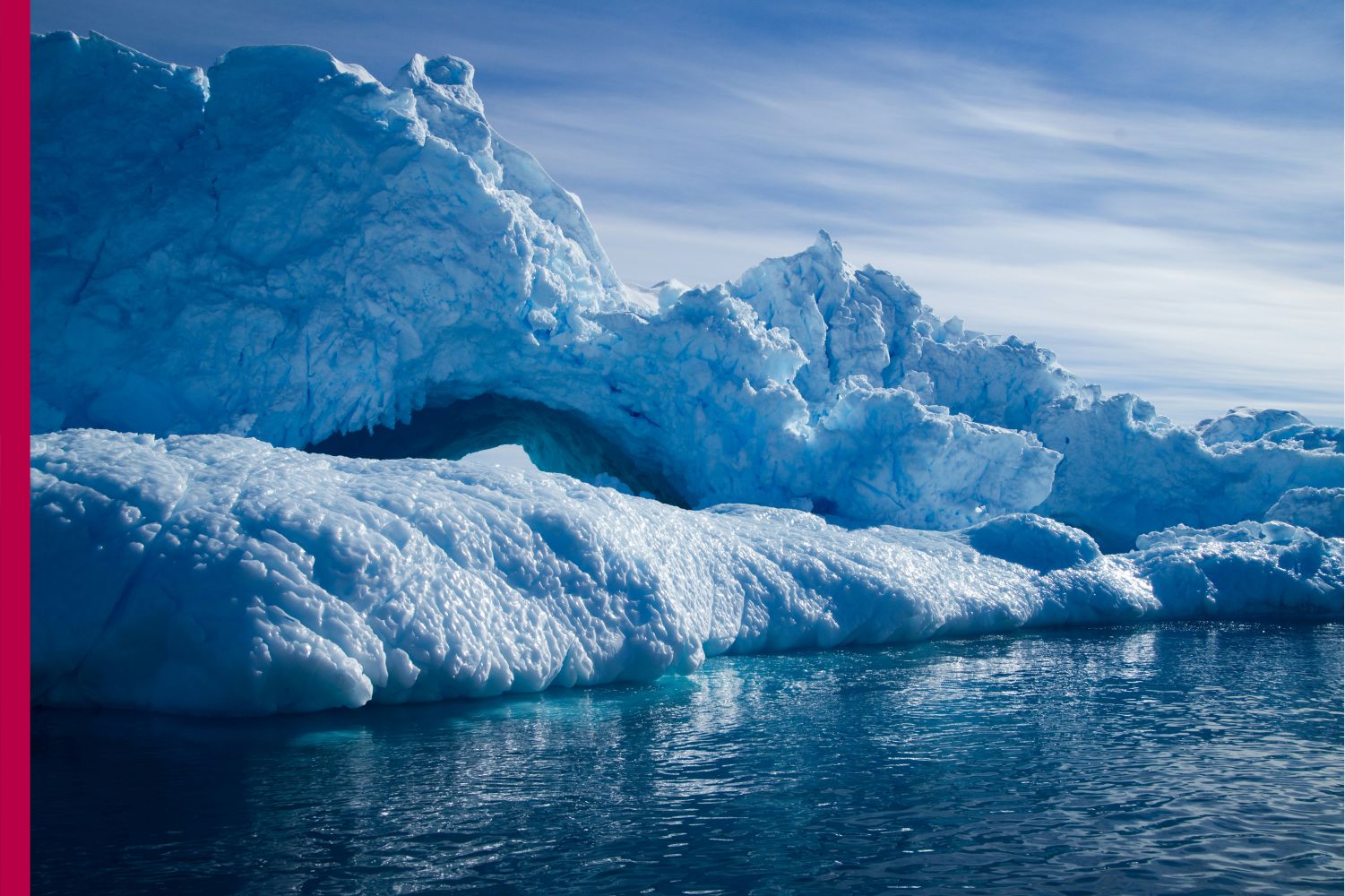
Antarctica, often seen as a vast, frozen wilderness untouched by human activity, is now showing alarming signs of melting. This remote continent, which holds nearly 70 percent of the world’s fresh water in the form of ice, plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. Recent changes in Antarctica’s ice sheets and glaciers are sending a clear warning about the accelerating impacts of global climate change.
For decades, Antarctica was believed to be relatively stable compared to the Arctic. However, scientific observations over the past few years reveal a different reality. Rising global temperatures, driven largely by greenhouse gas emissions, are warming the oceans surrounding Antarctica. These warmer waters are melting ice shelves from below, weakening them and causing massive ice chunks to break off into the sea. This process, known as ice shelf collapse, reduces the natural barrier that slows glaciers from flowing into the ocean.
One of the most concerning aspects of Antarctic melting is its contribution to sea level rise. When land-based ice melts and flows into the ocean, global sea levels increase. Even small changes in Antarctica can have significant consequences worldwide. Coastal cities, island nations, and low-lying regions face increased risks of flooding, erosion, and displacement of communities. The melting of Antarctic ice is not a distant problem it has direct implications for millions of people across the globe.
Melting in Antarctica also disrupts delicate ecosystems. The continent and surrounding Southern Ocean support unique wildlife, including penguins, seals, and krill. Changes in ice patterns affect breeding grounds and food availability, threatening entire food chains. Krill, a key species in the Antarctic ecosystem, depend on ice-covered waters for survival. A decline in krill populations can impact whales, fish, and seabirds, creating a ripple effect throughout the ocean.
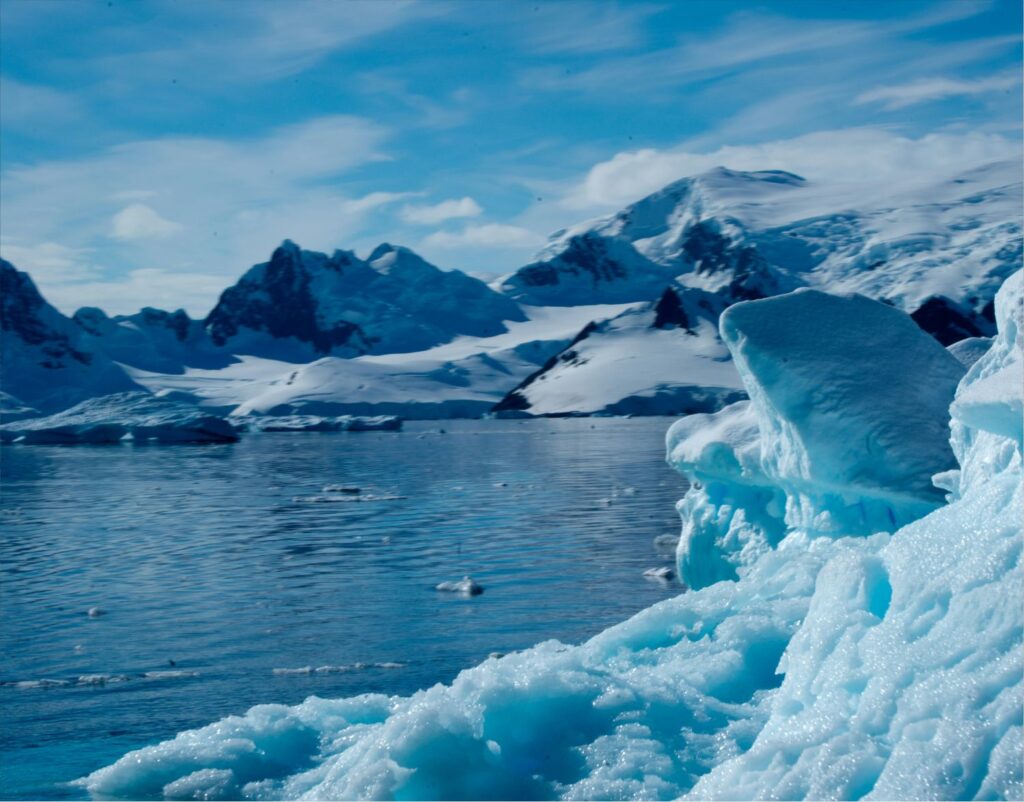

Another serious concern is the potential for irreversible change. Some glaciers in West Antarctica are believed to have reached a tipping point, where melting may continue even if temperatures stabilize. This phenomenon, known as marine ice sheet instability, could lead to long-term ice loss over centuries. Such changes highlight the urgency of understanding and addressing climate change before critical thresholds are crossed.
Scientific research in Antarctica has become more important than ever. Satellites, research stations, and international collaborations monitor ice thickness, temperature changes, and ocean currents. These studies help scientists predict future trends and inform global climate policies. Antarctica serves as a natural laboratory, offering clear evidence of how human activities influence even the most remote parts of the planet.
The melting of Antarctica also raises moral and environmental responsibility. Although the continent itself has no permanent human population, its changes affect the entire Earth system. Reducing carbon emissions, transitioning to renewable energy, and promoting sustainable practices are essential steps toward slowing global warming and protecting polar regions.
In conclusion, Antarctica showing signs of melting is a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet. What happens at the poles does not stay there it influences oceans, weather patterns, ecosystems, and human societies worldwide. The changes unfolding in Antarctica are not just scientific observations but urgent signals calling for collective action to protect Earth’s future.