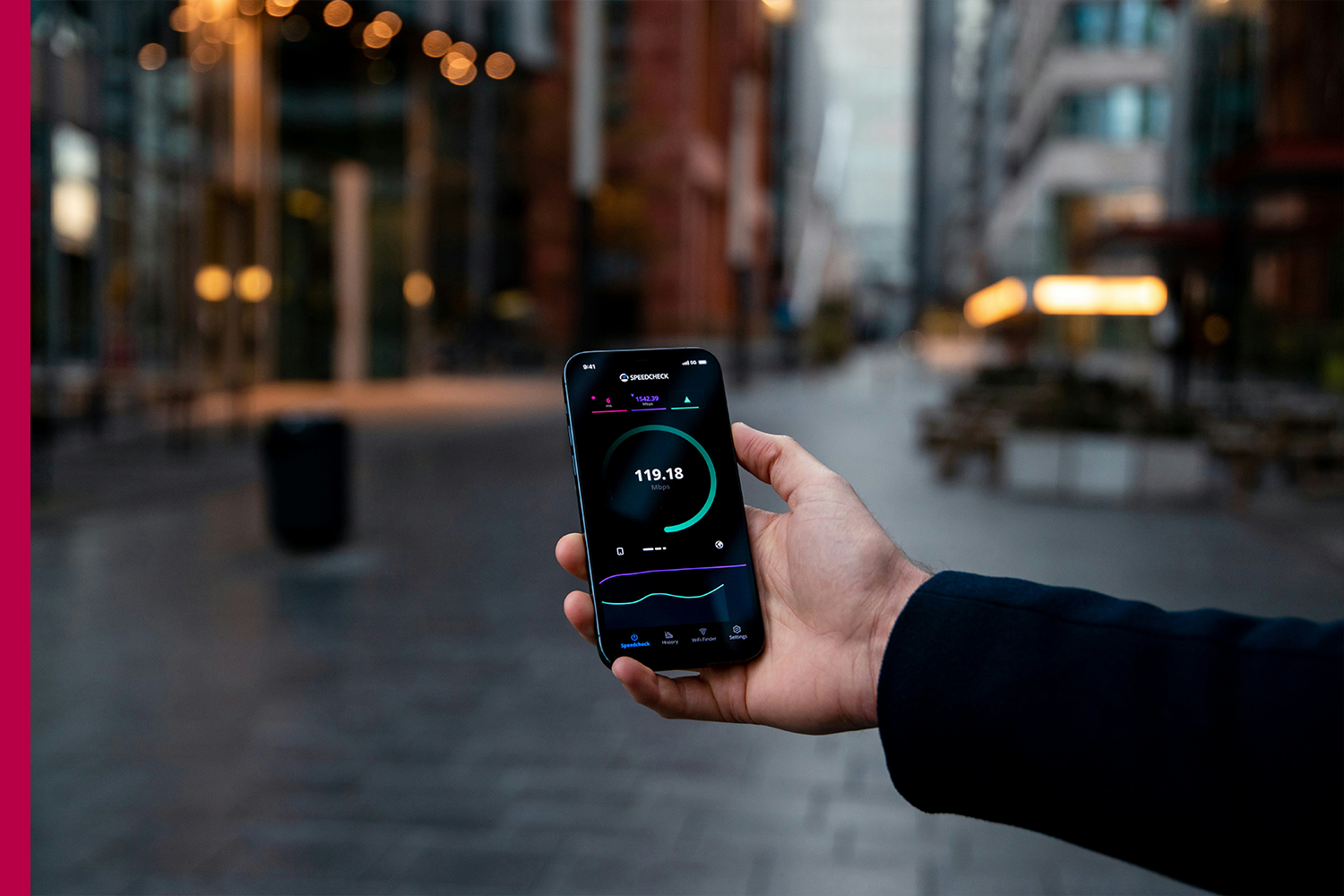
The evolution of mobile networks has transformed how we live, work, and interact with the world. From the early days of 2G text messages to today’s lightning-fast 5G video streaming, each generation of wireless technology has opened doors to new possibilities. As 5G continues its global rollout, researchers are already exploring the next frontier 6G. These technologies are not just about faster internet; they are reshaping industries, enabling new innovations, and redefining modern living.
The Journey So Far: From 1G to 5G
To understand the significance of 5G and 6G, it’s useful to look at how mobile networks have evolved:
- 1G (1980s) – Analog voice communication, basic calling.
- 2G (1990s) – Digital voice, SMS messaging, and limited data services.
- 3G (2000s) – Mobile internet access, video calls, and early app ecosystems.
- 4G (2010s) – High-speed broadband, HD video streaming, mobile apps, and cloud services.
- 5G (2020s) – Ultra-fast speeds, low latency, IoT connectivity, and smart cities.
Each generation brought exponential improvements. 5G represents a leap, not just in speed, but in transforming how devices, industries, and people interact.
What is 5G?
5G (Fifth Generation Network) is the latest global wireless standard, offering:
- Higher Speeds – Up to 10 Gbps, nearly 100x faster than 4G.
- Ultra-Low Latency – As low as 1 millisecond, critical for real-time applications.
- Massive Connectivity – Ability to connect millions of devices per square kilometer.
- Energy Efficiency – Designed for long-lasting IoT devices and sensors.
Unlike previous networks that focused mainly on faster mobile internet, 5G is built to connect everything—from smartphones and autonomous cars to smart factories and healthcare systems.
5G in Action: Transforming Industries
Healthcare
5G enables remote surgeries, telemedicine, and real-time patient monitoring. Doctors can operate using robotic systems with minimal delay, making healthcare accessible even in remote regions.
Automotive
Self-driving cars depend on instant communication with traffic systems, pedestrians, and other vehicles. 5G’s low latency is key to preventing accidents and ensuring smooth rides.
Smart Cities
Streetlights, waste management, energy grids, and traffic flow can all be optimized through IoT sensors connected by 5G.
Entertainment & Media
High-quality 4K/8K streaming, cloud gaming, and virtual reality experiences are seamless with 5G.
Manufacturing & Industry 4.0
Factories are adopting robotics and AI-driven systems that require real-time coordination, made possible by 5G networks.
Challenges of 5G
Despite its potential, 5G faces hurdles:
Infrastructure Costs – Building new towers and fiber connections is expensive.
Coverage Issues – High-frequency 5G signals have shorter range, requiring more antennas.
Security Concerns – More devices mean greater risk of cyberattacks.
Health Myths – Some public concerns (e.g., radiation fears) have slowed adoption in certain regions, despite lack of scientific evidence.
What is 6G? The Next Frontier
While 5G is still expanding, 6G (Sixth Generation Network) is already in development, expected to roll out by 2030. If 5G is about connecting devices, 6G is about connecting intelligence.
Predicted features of 6G include:
- Speeds up to 1 Tbsps. – A thousand times faster than 5G.
- Ultra-Low Latency (~0.1 ms) – Enabling instant communication.
- AI Integration – Networks will use artificial intelligence for self-optimization.
- Holographic Communication – Real-time 3D holograms for meetings and entertainment.
- Space-Air-Ground-Sea Networks – Integration of satellites, drones, and undersea communication systems for global coverage.
- Tactile Internet – Transmitting not just visuals and sound, but touch and physical sensations.
Potential Applications of 6G
Immersive Extended Reality (XR)
6G will power fully immersive AR, VR, and mixed reality experiences. Imagine attending a concert from your living room as a hologram, or training with realistic simulations.
Holographic Communication
Meetings may no longer be limited to video calls 6G could project life-size holograms of people into your room, enabling true “face-to-face” remote interaction.
Autonomous Ecosystems
While 5G enables self-driving cars, 6G could connect entire autonomous transportation networks, including cars, drones, and ships.
Smart Healthcare 2.0
6G will enable remote surgeries with real-time tactile feedback, personalized AI-driven treatments, and instant genetic data processing.
Global Connectivity
With satellite integration, 6G could eliminate internet dead zones worldwide, bringing connectivity to even the most remote areas.
Challenges Ahead for 6G
Like 5G, 6G will also face challenges:
High Development Costs – Building infrastructure for such high-frequency networks will require massive investments.
Energy Demands – Powering ultra-fast networks sustainably will be a major hurdle.
Ethical & Privacy Concerns – With deeper integration of AI, data security and surveillance concerns will rise.
Digital Divide – While advanced nations adopt 6G, poorer countries may struggle to even implement 5G.