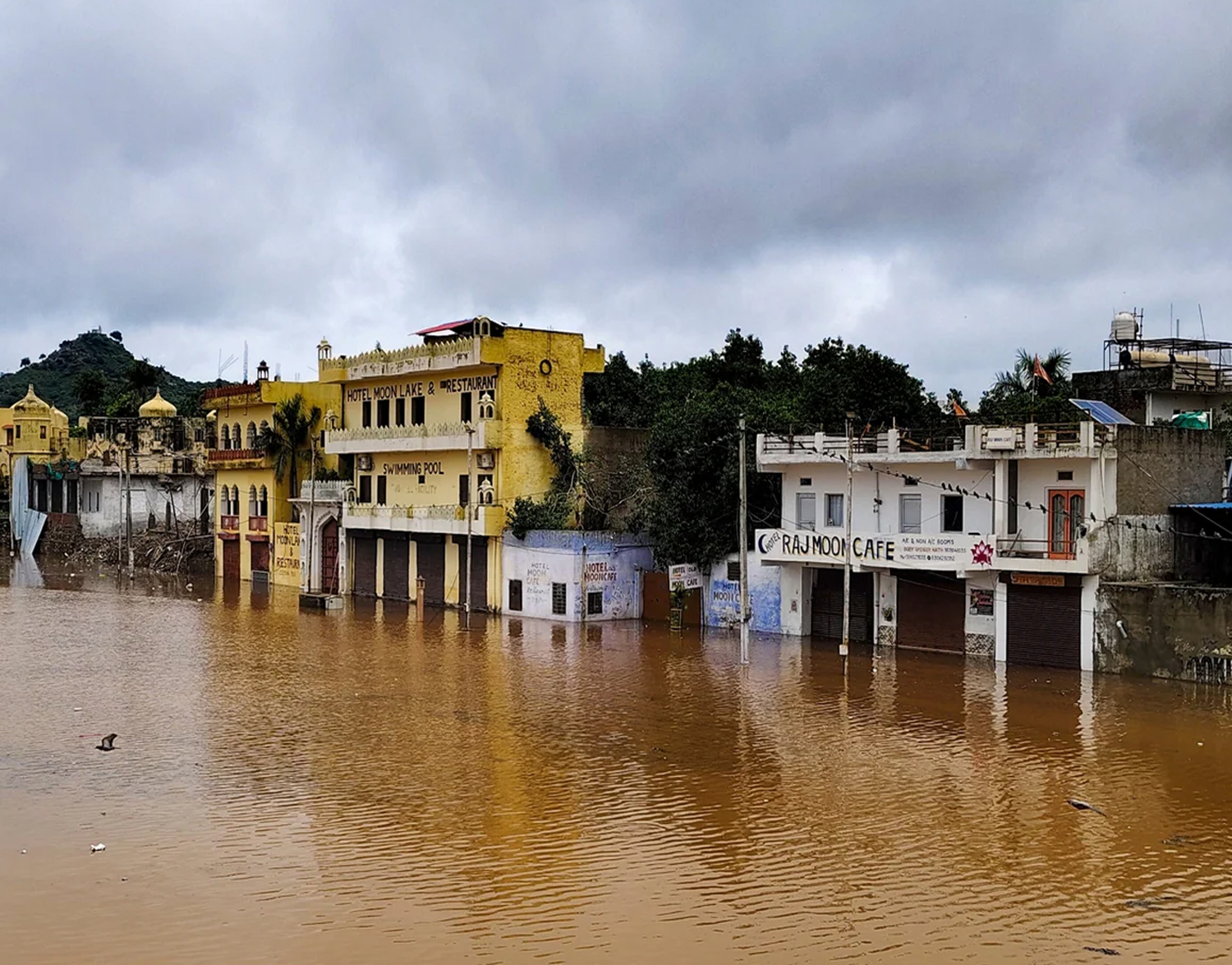
The monsoon season in India brings much needed relief from scorching summer heat, replenishing water reservoirs and supporting agriculture. However, excessive rainfall often leads to devastating floods, especially in states like Maharashtra and Bihar. Over the past few weeks, relentless downpours have triggered severe flooding, landslides, and widespread disruptions in these regions. Thousands have been displaced, infrastructure has been damaged, and rescue operations are in full
swing to assist affected communities.
This blog explores the causes, impact, and ongoing relief efforts in Maharashtra and Bihar, highlighting the challenges faced by residents and authorities.
Causes of the Monsoon Floods
1. Heavy and Continuous Rainfall
The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) had issued warnings for intense rainfall in Maharashtra and Bihar due to strong monsoon currents. Some areas recorded over 200-300 mm of rain within 24 hours, leading to rivers breaching danger levels.
2. Poor Drainage and Urban Flooding (Especially in Mumbai)
Mumbai, Maharashtra’s financial capital, faces chronic flooding due to:
- Clogged drainage systems (blocked by plastic waste and debris)
- Unplanned urban expansion (encroachment on natural water channels)
- High tide conditions worsening waterlogging
3. River Overflow and Dam Releases
In Bihar, rivers like the Kosi, Gandak, and Bagmati have overflowed due to heavy rainfall in Nepal and northern India. Additionally, water released from dams in Maharashtra (such as those in the Konkan region) has exacerbated flooding downstream.
4. Deforestation and Soil Erosion
Unchecked deforestation in hilly areas (like the Western Ghats in Maharashtra) reduces soil’s ability to absorb water, increasing landslide risks.
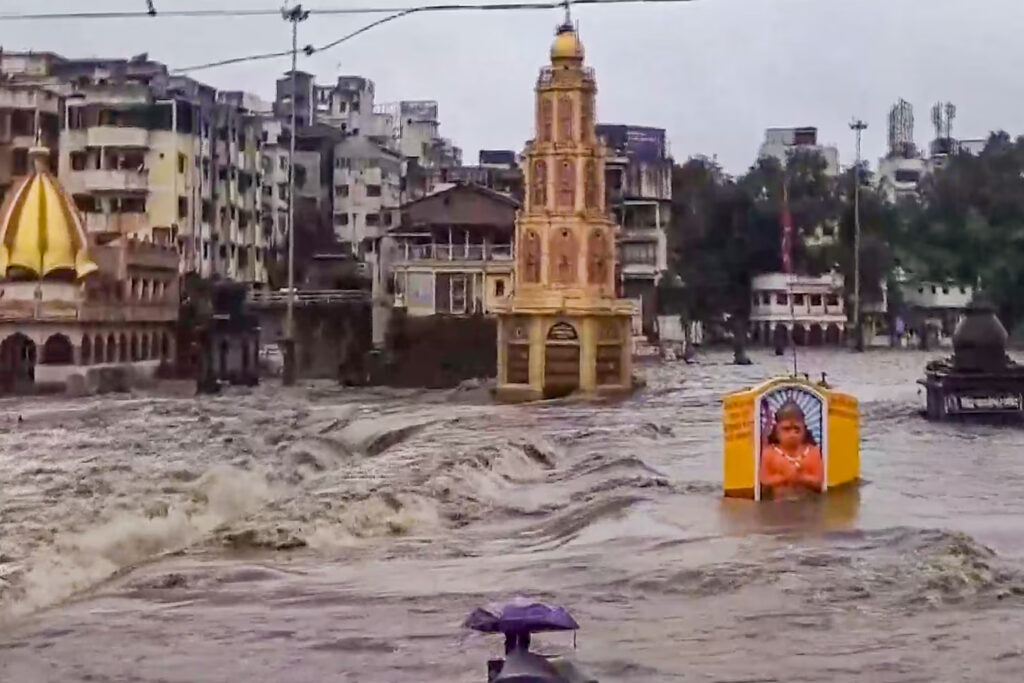

Impact of the Floods
1. Loss of Lives and Displacement
- Maharashtra: Over 50 deaths reported (including fatalities from landslides in Raigad and Ratnagiri).
- Bihar: At least 30 deaths, with thousands evacuated from low-lying areas. Many villages remain cut off due to submerged roads.
2. Infrastructure Damage
- Roads and Bridges: Washed away or submerged, disrupting transport.
- Railways: Trains canceled or delayed in Mumbai and Bihar.
- Power Outages: Electricity disrupted in flood-hit areas.
3. Agricultural Losses
- Farmlands inundated, destroying crops like rice and sugarcane.
- Farmers face huge losses, worsening rural distress.
4. Health Risks
Waterborne diseases (cholera, dengue) on the rise due to stagnant water. Limited access to medical aid in remote areas.
Rescue and Relief Operations
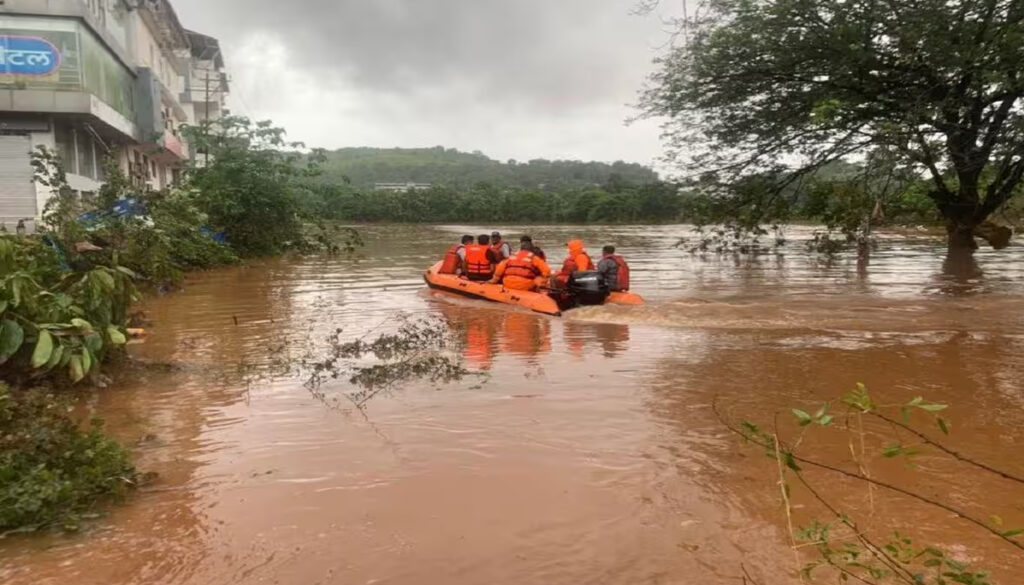

1. Government Response
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) and State Disaster Response Force (SDRF) deployed in both states.
- Indian Army and Navy assisting in evacuation in critical zones.
- Helpline numbers issued for emergency assistance.
2. Shelter and Rehabilitation
- Relief camps set up in schools and community centers.
- Food, clean water, and medical aid being distributed.
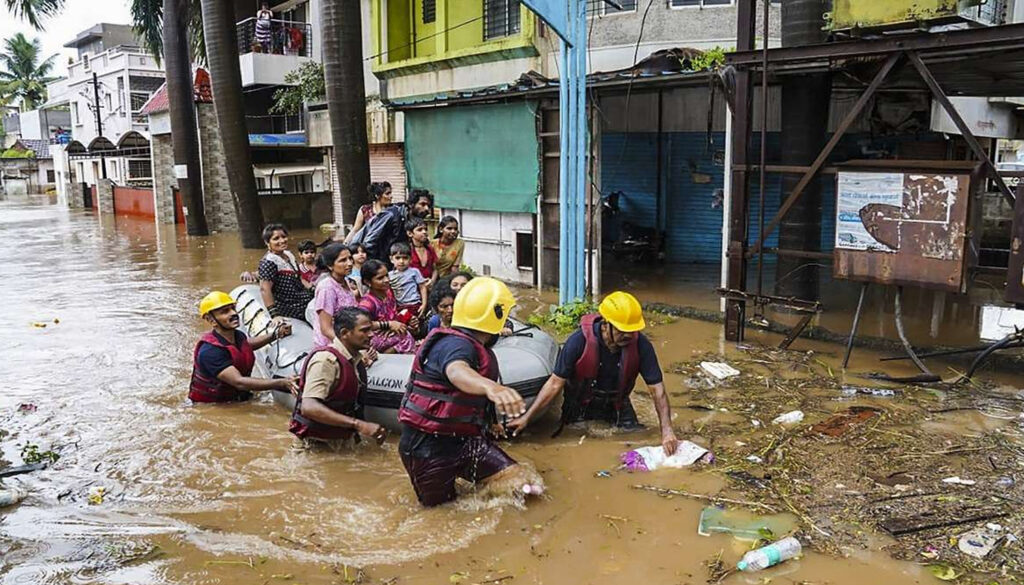
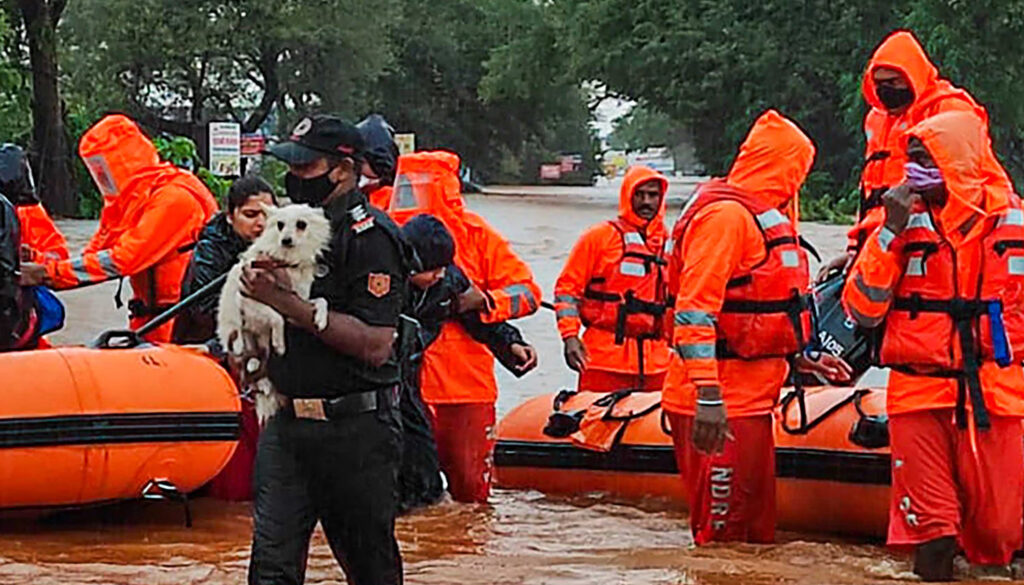


3. Challenges in Rescue Efforts
- Continuous rains hampering operations.
- Remote areas inaccessible due to damaged roads.
- Shortage of boats and rescue equipment in some regions.
Preventive Measures Needed
1. Better Urban Planning
- Mumbai and other cities need improved drainage systems.
- Strict enforcement against illegal construction near rivers.
2. Early Warning Systems
- IMD and local authorities must enhance real-time alerts.
- Community awareness programs on flood preparedness.
3. Sustainable Environmental Policies
- Afforestation in landslide-prone areas.
- Regulation of dam water releases to prevent sudden floods.
4. Strengthening Disaster Response
- More NDRF teams stationed in flood-prone states.
- Pre-monsoon preparedness drills for local administrations.

The monsoon floods in Maharashtra and Bihar highlight the recurring vulnerability of Indian states to extreme weather events. While rescue operations are underway, long-term solutions such as better infrastructure, environmental conservation, and efficient disaster management are crucial to minimizing future damage.
As citizens, we can contribute by supporting relief organizations, spreading awareness, and advocating for sustainable policies.
The resilience of affected communities is commendable, but systemic changes are needed to ensure their safety in the years to come.